Paris — “China one of the world’s most repressive autocratic regimes, uses its legislative arsenal to confine its population and cut it off from the rest of the world, especially the population of Hong Kong , which has plummeted in the Index,” said Reporters Without Borders.
Reporters Without Borders (RSF), the Paris-based international press freedom organisation, released its 20th World Press Freedom Index on May 3, 2022. The ranking, which assesses the state of journalism in 180 countries and territories, highlights the disastrous effects of news and information chaos - the effects of a globalised, unregulated online information space that encourages fake news and propaganda.
“The 20th World Press Freedom Index published by Reporters Without Borders (RSF) reveals a two-fold increase in polarisation amplified by information chaos – that is, media polarisation fuelling divisions within countries, as well as polarisation between countries at the international level,” said Rebecca Vincent, Director of Operations and Campaigns, RSF.
“Within democratic societies, divisions are growing as a result of the spread of opinion media following the “Fox News model” and the spread of disinformation circuits that are amplified by the way social media functions. At the international level, democracies are being weakened by the asymmetry between open societies and despotic regimes that control their media and online platforms while waging propaganda wars against democracies. Polarisation on these two levels is fuelling increased tension,” RSF added.
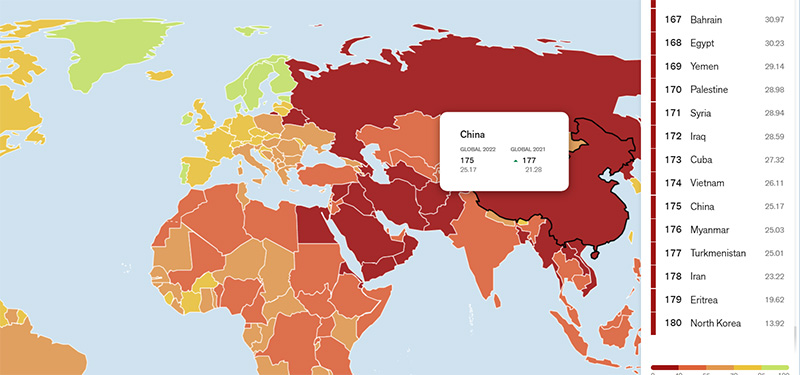
“The invasion of Ukraine (106th) by Russia (155th) at the end of February reflects this process, as the physical conflict was preceded by a propaganda war. China (175th), one of the world’s most repressive autocratic regimes, uses its legislative arsenal to confine its population and cut it off from the rest of the world, especially the population of Hong Kong (148th), which has plummeted in the Index. Confrontation between “blocs” is growing, as seen between nationalist Narendra Modi’s India (150th) and Pakistan (157th). The lack of press freedom in the Middle East continues to impact the conflict between Israel (86th), Palestine (170th) and the Arab states,” the watchdog stated.
“Media polarisation is feeding and reinforcing internal social divisions in democratic societies such as the United States (42nd), despite president Joe Biden’s election. The increase in social and political tension is being fuelled by social media and new opinion media, especially in France (26th). The suppression of independent media is contributing to a sharp polarisation in “illiberal democracies” such as Poland (66th), where the authorities have consolidated their control over public broadcasting and their strategy of “re-Polonising” the privately-owned media,” RSF said.
“The trio of Nordic countries at the top of the Index – Norway, Denmark and Sweden – continues to serve as a democratic model where freedom of expression flourishes, while Moldova (40th) and Bulgaria (91st) stand out this year thanks to a government change and the hope it has brought for improvement in the situation for journalists even if oligarchs still own or control the media,” they said.
“The situation is classified as “very bad” in a record number of 28 countries in this year’s Index, while 12 countries, including Belarus (153rd) and Russia (155th), are on the Index’s red list (indicating “very bad” press freedom situations) on the map. The world’s 10 worst countries for press freedom include Myanmar (176th), where the February 2021 coup d’état set press freedom back by 10 years, as well as China, Turkmenistan (177th), Iran (178th), Eritrea (179th) and North Korea (180th),” it stated.
RSF Secretary-General Christophe Deloire said: “Margarita Simonyan, the Editor in Chief of RT (the former Russia Today), revealed what she really thinks in a Russia One TV broadcast when she said, ‘no great nation can exist without control over information.’ The creation of media weaponry in authoritarian countries eliminates their citizens’ right to information but is also linked to the rise in international tension, which can lead to the worst kind of wars. Domestically, the ‘Fox News-isation’ of the media poses a fatal danger for democracies because it undermines the basis of civil harmony and tolerant public debate. Urgent decisions are needed in response to these issues, promoting a New Deal for Journalism, as proposed by the Forum on Information and Democracy, and adopting an appropriate legal framework, with a system to protect democratic online information spaces.”
“In the 180 countries and territories ranked by RSF, indicators are assessed on the basis of a quantitative survey of press freedom violations and abuses against journalists and media, and a qualitative study based on the responses of hundreds of press freedom experts selected by RSF (journalists, academics and human rights defenders) to a questionnaire with 123 questions. The questionnaire has been updated to take better account of new challenges, including those linked to media digitalisation,” they explained.
“In light of this new methodology, care should be taken when comparing the 2022 rankings and scores with those from 2021. Data-gathering for this year’s Index stopped at the end of January 2022, but updates for January to March 2022 were carried out for countries where the situation had changed dramatically (Russia, Ukraine and Mali),” RSF concluded.


![Tibet has a rich history as a sovereign nation until the 1950s when it was invaded by China. [Photo: File]](/images/stories/Pics-2024/March/Tibet-Nation-1940s.jpg#joomlaImage://local-images/stories/Pics-2024/March/Tibet-Nation-1940s.jpg?width=1489&height=878)